I was musing yesterday as I was visiting a budding community garden. Most follow the model of outlining beds using timber and then filling in with soil. Sometimes there is a compost pile and compost and mulch are applied sparingly. What if there is another model that is yet to be implemented which is water-wise and drought tolerant? Much like the beds I saw (and posted a picture of them) in the southern Dallas county garden – outlined with logs from the property, filled with mulch several inches deep and with ollas for watering. What if hugelkultur beds became the norm – like a community garden in Plano is working toward? Or keyhole gardens? or other techniques borrowed from drought-stricken areas around the world? If we are to continue to install gardens for the community – and promote and practice farming in the city – then we need to think outside the box as water restrictions become the norm rather than the unusual.
Hugelkultur comes from Eastern Europe, and mimics the forest floor – with wood then twigs then leaves then grasses, all of which compost and then dirt on top. As the wood deteriorates, it creates a rich environment for the micro-organisms and fungi that are necessary for drawing nutrients from the soil and making them available to plants. Also, as the wood deteriorates it becomes spongy and holds water. The net result is that a hugelkultur bed, once established, needs much less watering than a traditional garden bed. A great reference from a pioneer in the refinement of this technique is “Sepp Holzer’s Permaculture: A Practical Guide to Small-Scale, Integrative Farming and Gardening.”
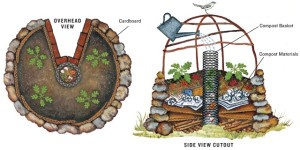
One important advantage of a keyhole garden is that it is perfect for someone who cannot bend over to weed or plant, yet wants to continue to garden. It’s a raised bed extraordinaire!
Contact me if you want a hugelkultur bed or a keyhole garden to be part of your gardening experience this year!